| Q.no.1: define business? What are the main components of the business? Or what is mean by business? Explain the scope of business? |
Answer:
Meaning of business:
In the literary sense the word business means “the state of being busy “technically the term business means all those activities which are related to the production and distribution of goods and services with the object of earning profit. In addition to this the purchase and sale of goods on whole sale or retail basis by business also provides direct services. These may be health services, legal or services etc.
According to the R.N. Owen
“Business includes all the commercial and industrial activities that provide goods and services to the people with an objective to earn profit”
“A business is an institution organized by a person or group of persons to produce or distribute goods and services with an object of earning profit to satisfy human wants”
SCOPE OF BUSINESS OR COMPONENTS OF BUSINESS
The scope of business is very wide. it covers activities related to production, distribution of goods and services with an aim to earn profit.
The business activities are usually divided into two parts.
Business
- Industry
- Commerce
Meaning of Industry
The term”industry” refers to that part of business activity which is concerned with the extraction production or fabrication of products
The products which are raised, produced or processed by an industry may either be used by the final consumer or by another concern for further production. If the goods are consumed by final consumer these are named as “consumer’s goods (cloth and shoes)”. If the goods are used for further production of wealth they are called “producers’s or capital good (plant and machinery)”. In case, the goods produced by any industry are further processed into finished product by another concern such goods are named as “intermediate goods (cotton and iron)”.
Industry
Secondary industry
Extractive industry
Genetic industry
Primary industry
constructive industry
Manufacturing industry
service industry
Primary industry
Primary industry is engaged in the production or extraction of raw materials, which are used in secondary industry. Primary industry can be divided into two parts:
(a) Extractive industry
In this industry, hidden resources below or beneath the surface of the earth are extracted. All kinds of mining are the examples of such industry. E.G extraction of oils, gas, coal, etc.
(b) Genetic industry
Genetic industries are the industries engaged in the reproduction or multiplication of certain species of plants and animals. Plant nurseries, poultry farms and cattle breeding farms (animal husbandry) are the main examples of genetic industries.
- Secondary industry
These industries use raw material to make useful goods. This industry also contributes by making goods more profitable and useful by completing same finished and incomplete goods or by changing their former design. Raw material for these industries id obtained from primary industry. It can be divided into two parts:
(a) Manufacturing industry:
This industry is concerned worth the processing or transformation of raw materials and semi-finished products into finished products. Such industry changes the shape and form of materials produced by genetics and extractive industries. Manufacturing industry is of the following types:
(1) Analytical :
An oil refinery where crude oil is refined and several petroleum products are obtained.
(2) Synthetically:
Factories where cosmetics, soap, cement, fertilizer and paint, etc are prepared.
(3) Processing:
Cotton textile industry where cotton passes through the spinning, weaving, dyeing bleaching and printing processes
(4) Assembling:
Manufacturing of radios, TV sets watches and automobiles.
(b) Constructive industry
This industry is engaged in the construction of building, bridges, roads, dams, etc. It utilizes the products of manufacturing industries such as bricks, steel, cement etc, the distinctive feature of this industry is that its products remain fixed at one place and cannot be taken physically to the market for sale.
(c) Services industry:
Business provides not only goods but also services. A services industry does not produce tangible goods. It is engaged in providing services to the public, hotel, railways shipping companies, transport companies, insurance companies etc are some example of service industry.
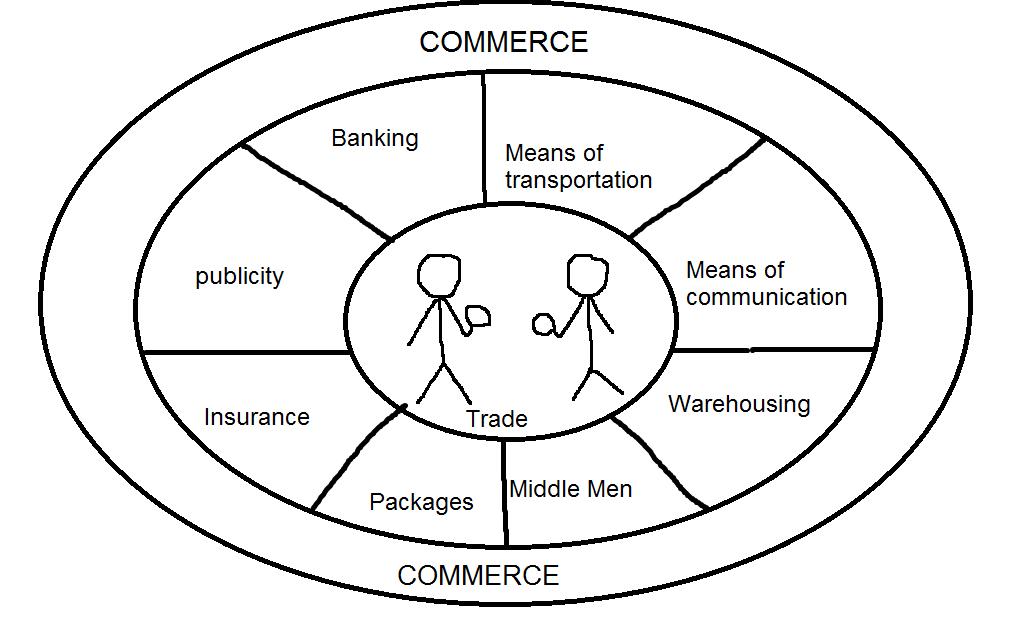
(B)-COMMERCE
Commerce is the very important part of business. It is concerned with the buying and selling of goods. It includes all those activities which are related to the transfers of goods from the place of production to ultimate consumers.
Definition of Commerce
According to the James Stephen
“Commerce includes those activities which remove the hindrances of time, persons and palaces in the exchange of goods”
In the words of Thomas
Commercial occupations deal with buying and selling of goods, the exchange of commodities and the distribution of the finished goods”
TRADE
The literary meaning of trade is exchange of goods. It may be defined as the exchange of commodities between individuals or groups either through barter system or through any medium such as money. It includes all the selling and buying activities either within a country or across the boundaries of the country. In actual practice, Trade is the whole procedure of distribution the goods produced by different persons or industries to their ultimate consumers. It is, therefore, said “the trade removes the personal hindrance, in exchange of commodities”
“Trade is activity of buying and selling of goods for money or other goods” (oxford dictionary)
Trade can be classified into two components:
HOME TRADE
In home trade, exchange of goods or trade or conducted within the boundaries of a particular country. Seller and buyer belong to the same country. It is also known as domestic, Local or internal trade. Home trade has two types.
Wholesale trade:
Wholesale trade means selling of goods in large quantities to shopkeepers in order to resell them in small quantities to the consumers. Wholesaler has specialized dealings in particular items. He purchases in bulk from producer or industries and sell them in small quantity to retailers.
Retail trade:
Retailing means selling the goods in small quantities to the ultimate consumers. Retailer is a middleman who purchases goods from manufacturer or wholesaler and provides these goods to the consumers near their houses.
FOREIGN TRADE
Foreign trade is a trade of exchange of goods and services between two or more independent countries for their mutual advantages. It includes import and export of commodities among the producer and consumer countries. Foreign or international trade is integral part of economy and plays a vital role in economic growth and social welfare of a country. Foreign trade has three types.
Import trade
When a country buys goods and services from other countries, it is known as import trade. For instance, Pakistan buys petrol from Iran.
Export trade
When a country sells goods and services to other countries, it is known as export trade. For example, Pakistan sells rice to European countries.
Entrepot trade:
In entrepot trade, goods are imported from various countries with a view to re-export them to other countries. In the type of trade, goods are kept in bounded warehouses till they are r-exported. No import duty is charged on the goods. Crude petroleum products are the examples of entrepot trade.
AIDS TO TRADE
The activities which facilitate the purchase and sale of goods and services are called aids to trade. The aids which are essential for the expansion of the trade are
Transportation
The different means of transport e.g. railways, ships, airlines etc help in carrying the goods from places of production to the centres of consumption. Transport thus ensures movement of goods and services from one place to another. It not only widens the market of goods but also increases the mobility of labour and capital.
Insurance
Insurance is another important aid to trade. The risk of damage of goods due to fire, Flood, earthquake or other causes is covered by insurance. The insurance companies compensate the loss of commodities due flood etc. to the traders on the payments of insurance premiums. Insurance thus helps in the expansion of trade.
Warehousing
Warehousing is a king of storage. Now a day’s most of the goods are produced in anticipation of demand. They are stored in safe places and are released as and when demanded in the market. Warehousing thus helps in overcoming the barriers of the time and creates time utility.
Banking
The commercials bank plays an important role in financing the various trade activities. They finance the traders for stockholding and transportation of goods. They also assist the buyers and sellers of goods in receiving and making payments both at national and international level. The finance or credit is provided to the trader in the form of cash credit, overdrafts and loans.
Advertisement
Selling of goods is the most important and difficult problem of the manufacturer. Advertisement about the product through newspapers, magazines, radio, television, etc has greatly helped the consumers in choosing the goods of their tastes. The consumers come to know about the quality and price of goods in short time and pick up the product that suits them. Advertisement thus has increased the sale of goods.
Middlemen
There is long chain of middlemen (wholesaler, retailers, and brokers) who act as agents between the producers and the consumers. They bring the sellers and buyers of goods together and help them in completing the transaction of goods. These agents act for commission. The mercantile agents thus have greatly helped in distribution of goods from producers to the consumers.
Communication
Means of communication provide or convey commercial information to individuals, firms and companies. These consist of people, institutions and processes engaged in spreading the necessary business information between producers and consumers. Radio and television are general communication services by telephones, fax, telegrams, E-mail, internet are also important means of communication. In modern era, success of a business depends on the latest, concise and accurate information.
Packing
Packing means putting goods in wrappers, containers, etc. Packing helps to protect the goods from damage during transport and warehousing. It makes the goods attractive also. Packing helps in the conveyance and handling of goods. It removes the hindrance of risk by keeping goods safe and free from spoilage. Trade and transport of goods have become easier and safer due to improve in the art and methods of packaging.
Crux
After the industrial revolution of 19th century business has becomes very complex these days. Without understanding above mentioned classification of business no one can understand scope of business.